Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Dan ReynoldsDan Reynolds pada 2018LahirDaniel Coulter Reynolds14 Juli 1987 (umur 36)Las Vegas, Nevada, A.S.Pekerjaan Penyanyi Penulis lagu produser rekaman Tahun aktif2008–sekarangSuami/istriAja Volkman (m. 2011)Anak4Karier musikGenre Alternative rock[1] indie rock[2] pop rock[2] indie pop[3] electropop[1] Instrumen Vokal gitar piano keyboards drum perkusi LabelInterscopeArtis terkait Imagine Dragons Egyptian X...

Europamästerskapet i handboll för herrar 1998Europamästerskapet i handboll för herrarEvenemangsfaktaDatum29 maj–7 juni 1998Värdland ItalienSpelplatser2DeltagareNationer12StatistikMatcher38Mål1879 (49,4 per match)Flest mål Jan Filip (48 mål)Bäste spelare Daniel Stephan (MVP)0 Mästare Sverige (2:a titeln) Tvåa Spanien Trea Tyskland000Fyra Ryssland Föregående Följande 1996 Spanien Kroatien 2000 Europamästerskapet i handboll för her...

No debe confundirse con Dominica. «Dominicana» redirige aquí. Para otras acepciones, véase Dominicana (desambiguación). República DominicanaBandera Escudo Lema: Dios, Patria y Libertad Himno: Himno nacional de la República Dominicana ¿Problemas al reproducir este archivo? Capital(y ciudad más poblada) Santo Domingo Escudo de Santo Domingo18°28′35″N 69°53′36″O / 18.476388888889, -69.893333333333 Sede de gobierno Palacio NacionalIdioma oficial EspañolGentilic...
Questa voce sull'argomento artisti marziali russi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Robert Mšvidobadze Nazionalità Russia Peso 60 kg Judo Specialità -60kg Palmarès Competizione Ori Argenti Bronzi Mondiali 0 1 0 Europei 2 0 0 Universiadi 0 0 1 Campionati russi 0 0 2 Per maggiori dettagli vedi qui Statistiche aggiornate al 19 novembre 2020 Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Robert Nikolaevič Mšvidobadze (in russo Роб

Герб Вільнюського повіту ДеталіНосій Вільнюський повітЗатверджений 20 грудня 1999Використання Територіальний Герб Вільнюського повіту (лит. Vilniaus apskritis herbas) — символ сучасного адміністративно-територіального утворення в Литовській республіці Вільнюського повіту. Гер...

关于与「封神榜 (1989年電視劇)」標題相近或相同的条目,請見「封神榜 (消歧義)」。 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2023年7月22日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:封神榜 (1989年電視劇) — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2016) هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة ب�...

Potret diri dari Arnold Joseph Toynbee.Arnold Joseph Toynbee (lahir di London 14 April 1889; meninggal di New York 22 Oktober 1975) adalah sejarawan Inggris yang terkenal melalui bukunya yang berjudul A Study of History, berisi tentang penyelidikan secara sejarah tentang asal usul, perkembangan, dan kehancuran beradaban besar.[1] Keluarga Toynbee berasal dari Lincolnshire, tempat milik kakek buyutnya, George Toynbee (1783 -1865) yang adalah seorang petani makmur.[2] Harry Valp...

Coconut IslandNative name: PorumaSatellite image of Coconut IslandA map of the Torres Strait Islands with the Coconut Island labelled as PorumaGeographyLocationNorthern AustraliaAdjacent toGreat North East Channel, Torres StraitAdministrationAustraliaStateQueensland Town in Queensland, AustraliaCoconut Island / Pormula IslandQueenslandCoconut Island / Pormula IslandCoordinates10°03′01″S 143°04′10″E / 10.0502°S 143.0694°E / -10.0502; 143.0694 (Poruma...

Координати: 45°28′ пн. ш. 18°13′ сх. д. / 45.46° пн. ш. 18.21° сх. д. / 45.46; 18.21 Подгорач Podgorač — Громада — Муніципалітет ПодгорачOpćina Podgorač Координати: 45°28′ пн. ш. 18°13′ сх. д. / 45.46° пн. ш. 18.21° сх. д. / 45.46; 18.21

فيليب لودفيغ، كونت بالاتينات-نيوبورغ (بالألمانية: Philipp Ludwig von Pfalz-Neuburg) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 2 أكتوبر 1547 تسفايبروكن الوفاة 22 أغسطس 1614 (66 سنة) نويبورغ آن در دوناو مكان الدفن بافاريا مواطنة ألمانيا الزوجة آنا من كليفز، كونتيسة نيوبورغ (1574–) الأو�...

السفارة السعودية طاجيكستان السعودية طاجيكستان الإحداثيات 38°34′05″N 68°48′31″E / 38.568°N 68.8085°E / 38.568; 68.8085[1] البلد طاجيكستان المكان دوشنبه السفير وليد بن عبد الرحمن الرشيدان الموقع الالكتروني سفارة المملكة العربية السعودية في طاجيكستان تعديل مصدري - تعدي�...

American pianist Birdie BlyeBornBirdice BlyeMarch 24, 1871Sioux City, Iowa, U.S.DiedJune 23, 1935(1935-06-23) (aged 64)Chicago, Illinois, U.S.Resting placeFairlawn CemeteryOccupationPianistNotable worksreminiscences of Anton RubinsteinSpouse William B. S. Richardson (m. 1901) Blye with violin Birdie Blye (1905) Birdice Blye-Richardson Birdice Blye-Richardson (March 24, 1871 - June 23, 1935) better known as Birdie Blye, was an American pianist. At 5 ...

ケロロ軍曹 > ケロロ軍曹 (アニメ) > 超劇場版ケロロ軍曹3 ケロロ対ケロロ天空大決戦であります! 超劇場版ケロロ軍曹3ケロロ対ケロロ天空大決戦であります!監督 山口晋脚本 横谷昌宏製作総指揮 佐藤順一(総監督)出演者 渡辺久美子川上とも子小桜エツ子中田譲治子安武人草尾毅斎藤千和平松晶子石田彰池澤春菜能登麻美子広橋涼福田沙紀音楽 鈴木さえ子�...

This article is about Basilica in France. For other uses, see Church of St. Thérèse of Lisieux (disambiguation). Basilica of Sainte-Thérèse of Lisieux Basilique Sainte-Thérèse de Lisieux (in French)Basilica of Sainte-Thérèse in LisieuxReligionAffiliationRoman CatholicEcclesiastical or organizational statusMinor basilicaYear consecrated1951LocationLocationLisieux, FranceGeographic coordinates49°8′22.56″N 0°14′11.04″E / 49.1396000°N 0.2364000°E / 49.1...

اختصاراتب:أف البوابة أحدث التغييرات المشروع التصنيفات مقدمة ألعاب الفيديو أو ألعاب إلكترونية أو ألعاب الحاسوب (بالإنجليزية: video game) هي ألعاب مبرمجة بواسطة الحاسوب وتلعب عادة في مشغلات ألعاب الفيديو حيث تعرض في التلفاز بعد إيصال الجهاز به. جهاز الإدخال في ألعاب الفيديو هو...
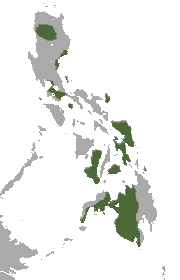
Species of bat Philippine dawn bat Conservation status Vulnerable (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Chiroptera Family: Pteropodidae Genus: Eonycteris Species: E. robusta Binomial name Eonycteris robustaMiller, 1913 Philippine dawn bat range The Philippine dawn bat (Eonycteris robusta) is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae found in the Philippines. References ^ Waldien, D.L.; Carino...

Government schoolNandipur High SchoolLocation Jajpur, Odisha, IndiaCoordinates20°48′10″N 86°26′11″E / 20.80278°N 86.43639°E / 20.80278; 86.43639InformationTypeGovernmentEstablished1955HeadmasterTrilochan Prasad [a]Staff4Faculty11[1]Grades4th -10thAffiliationBSE (Board of Secondary Education, ODISHA)Websitewww.odisha.gov.in/schooleducation/pdf/school.xls Nandipur High School, located in Nandipur, Jajpur, Odisha, India is one of the oldest sch...

Lista światowego dziedzictwa UNESCO w Czarnogórze – lista miejsc w Czarnogórze wpisanych na listę światowego dziedzictwa UNESCO, ustanowionej na mocy Konwencji w sprawie ochrony światowego dziedzictwa kulturowego i naturalnego, przyjętej przez UNESCO na 17. sesji w Paryżu 16 listopada 1972[1] i ratyfikowanej przez Czarnogórę 3 czerwca 2006 roku[2]. Obecnie (stan na 2023 rok) na liście znajdują się 4 obiekty: 3 dziedzictwa kulturowego oraz 1 o charakterze przyrodniczym[2]. Na cz...

Ahmad MuhtadiAbuya Ahmad Muhtadi bin Dimyathi al-BantaniNamaAhmad MuhtadiNasabbin Muhammad DimyathiNisbahal-BantaniLahir26 Desember 1953 (umur 69)(28 Jumadil Awal 1374 Hijriyah) Cadasari, Pandeglang, BantenNama lainAbuya Muhtadi DimyathiKebangsaan IndonesiaEtnisSunda BantenJabatanPimpinan Pondok Pesantren Roudotul Ulum Cidahu[1]FirkahSunniMazhab FikihSyafi'iOrang tuaAbuya Dimyathi (ayah), Hajjah Asma (ibu) Abuya, Kiai, Haji Ahmad Muhtadi bin Dimyathi al-Bantani, atau yang lebih d...



