CSS Manassas
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
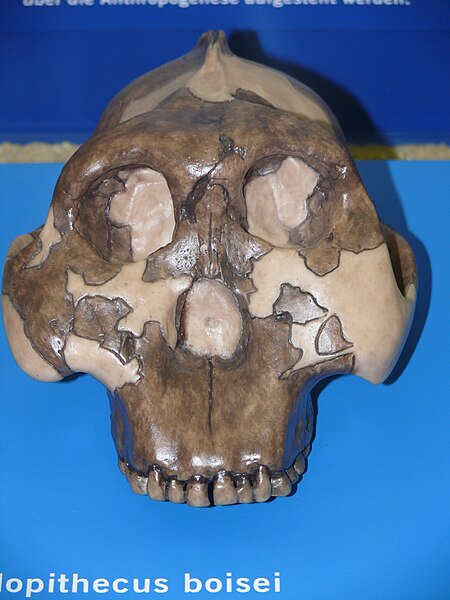
Paranthropus boiseiRentang fosil: Pliosen-Pleistosen Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Mammalia Ordo: Primates Famili: Hominidae Genus: Paranthropus Spesies: P. boisei Nama binomial Paranthropus boisei(Mary Leakey, 1959) Paranthropus boisei (awalnya disebut Zinjanthropus boisei dan lalu Australopithecus boisei) adalah hominin awal dan dideskripsikan sebagai spesies Paranthropus terbesar. Spesies ini hidup sekitar 2.6 hingga 1.2 juta tahun yang lalu selama Plios...
هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) بطولة ا

Grabstätte Claus Böhmler auf dem Friedhof Ohlsdorf Claus Böhmler (* 29. Oktober 1939 in Heilbronn; † 23. Februar 2017 in Hamburg) war ein deutscher Bildender Künstler, Zeichner und Medienkünstler. Er war Professor an der Hochschule für Bildende Künste Hamburg. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Leben und Werk 2 Rezeption 3 Auszeichnungen 4 Einzelausstellungen (Auswahl) 5 Ehemalige Studenten 6 Einzelnachweise 7 Literatur 8 Weblinks Leben und Werk Böhmler machte eine handwerkliche Ausbildungen im G...

بانياكافالو شعار الإحداثيات 44°25′01″N 11°58′34″E / 44.4168618°N 11.9760633°E / 44.4168618; 11.9760633[1] [2] تقسيم إداري البلد إيطاليا[3][4] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة ربنة خصائص جغرافية المساحة 79.58 كيلومتر مربع (9 أكتوبر 2011)[5] ارتفاع 12 متر �...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (نوفمبر 2021) إجمالي الهامش الربحي (بالإنجليزية Gross profit margin) هو الفرق بين الإيرادات وتكلفة البضائع المباعة (COGS) مقسومًا على الإيرادات. يتم التعبير عن الهامش الإجمالي كنسبة

Kedutaan Besar Republik Indonesia di MadridEmbajada de la República de Indonesia en MadridKoordinat40°26′55″N 3°39′13″W / 40.448519°N 3.653657°W / 40.448519; -3.653657Lokasi Madrid, SpanyolAlamatCalle de Agastia, 6528043 Madrid, SpanyolDuta BesarMuhammad NajibSitus webkemlu.go.id/madrid/id Kedutaan Besar Republik Indonesia di Madrid (KBRI Madrid) (Spanyol: Embajada de la República de Indonesia en Madrid) adalah misi diplomatik Indonesia untuk Kerajaan...

For the district, see Betafo District. For the village in Arivonimamo,Itasy, see Betafo, Arivonimamo. Betafoladang dekat BetafoBetafoLetak di MadagaskarKoordinat: 19°50′24″S 46°51′18″E / 19.84000°S 46.85500°E / -19.84000; 46.85500Koordinat: 19°50′24″S 46°51′18″E / 19.84000°S 46.85500°E / -19.84000; 46.85500Negara MadagaskarKawasanVakinankaratraDistrikDistrik BetafoKetinggian1.410 m (4,630 ft)Populasi (...

Bert Hölldobler Información personalNacimiento 25 de junio de 1936 (87 años)Andechs (Alemania) Nacionalidad AlemanaLengua materna Alemán FamiliaCónyuge Turid Holldobler-Forsyth (desde 1965) EducaciónEducado en Universidad de Wurzburgo Información profesionalOcupación Entomólogo, zoólogo, mirmecólogo y profesor universitario Área Mirmecología Empleador Universidad de WurzburgoUniversidad de HarvardUniversidad de MainzUniversidad de ZúrichUniversidad Estatal de ArizonaUnivers...

Deep-fried battered onion slices This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Onion ring – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Onion ringBasket of onion ringsTypeEntree, side dish, snack dishCourseHors d'oeuvrePlace of originUnit...

Mapa da distribuição dos biomas brasileiros. O Piauí é considerado uma área de transição entre a Caatinga e a Mata dos Cocais. O Estado conta, portanto, quatro tipos de formações vegetais: Manguezais, Caatinga, Cerrado e a Mata dos Cocais. [1] Manguezais Presença forte nos litorais, é a formação vegetal de menor presença no Piauí. É desenvolvido em solo salino e em ambientes inundados e com baixa presença de oxigênio. Caatinga Caatinga Ocupa quase 30% da vegetação do estad...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Saka dan Saka. Artikel ini bukan mengenai Bahasa Sakha, Bahasa Makhuwa, atau Rumpun bahasa Skithia. Bahasa Saka Khotan, Tumshuq Dituturkan di Tiongkok India Iran[1] WilayahCekungan TarimEtnisSakaEra100 SM - 1000 M[2]Rumpun bahasaIndo-Eropa Indo-IranIranIran TimurSaka DialekKhotan Tumshuq Sistem penulisanBrahmi, KharosthiKode bahasaISO 639-2khoISO 639-3Mencakup:kho – Khotanxtq – TumshuqLINGUIST Listkho (K...

1999 video game 1999 video gameStar Wars Episode I: The Gungan FrontierDeveloper(s)Lucas LearningPublisher(s)Lucas LearningPlatform(s)Macintosh, WindowsRelease1999Genre(s)Simulation, strategy Star Wars: Episode I - The Gungan Frontier is a 1999 video game by Lucas Learning. Plot and gameplay In a game similar to SimLife, the player aims to create a new ecology for Gungan colonisers by using the sacred creature known as the Kresch to build a new home on the moon given to the player by Boss Nas...
Species of lizard Great desert skink Conservation status Vulnerable (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Order: Squamata Family: Scincidae Genus: Liopholis Species: L. kintorei Binomial name Liopholis kintorei(Stirling & Zietz, 1893) Synonyms[2] Egernia kintorei Stirling & Zietz, 1893 Egernia dahlii Boulenger, 1896 Egernia kintorei — Glauert, 1960 Liopholis kintorei — Gardner et al., ...

Football clubCruz Azul PremierFull nameCruz Azul Fútbol Club, A.C. PremierNickname(s)La Máquina (The Machine)Los Cementeros (The Cementers)Los Celestes (The Sky-Blues)Founded14 July 2015; 8 years ago (2015-07-14)Dissolved2018; 5 years ago (2018)GroundLa Noria Xochimilco, Mexico CityCapacity1,000[1]OwnerCooperativa Cemento Cruz AzulChairmanGuillermo Álvarez CuevasLeagueLiga Premier - Serie AApertura 2017PreseasonWebsiteClub website Home colours Aw...

Кругообіг води в природі — приклад теорії з високою пояснювальною силою Пояснювальна сила — це здатність теорії повно і точно описувати власний об'єкт. Одним з головних критеріїв пояснювальної сили є передбачальна сила[en], тобто вважається, що з двох теорій зі спіл...

Fictional character in Marvel Comics For the DC Comics character, see Batwing (DC Comics). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Batwing Marvel Comics – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Comics character BatwingCove...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Doom Resurrection – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 2009 video gameDoom ResurrectionApp iconDeveloper(s)Escalation StudiosPublisher(s)id SoftwareDirector(s)Tom MustaineJohn CarmackProd...

Structures dated about 10,000 to 2,000 BC This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Neolithic architecture – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Excavated dwellings at Skara Brae Neolithic architecture refers to structures enco...

Japanese light novel series Bibliophile PrincessFirst light novel volume cover, featuring Elianna Bernstein (left) and Christopher Selkirk Ashelard (right)虫かぶり姫(Mushikaburi-hime)GenreFantasy, romance[1] Novel seriesWritten byYuiPublished byShōsetsuka ni NarōOriginal runSeptember 13, 2015 – January 23, 2022 Light novelWritten byYuiIllustrated bySatsuki ShiinaPublished byIchijinshaEnglish publisherNA: J-Novel ClubImprintIris NEODemographicFemaleOri...

English judoka and professional wrestler For other people named Chris Adams, see Chris Adams (disambiguation). Chris AdamsChris Adams, c. 1985BornChristopher Adams(1955-02-10)10 February 1955Rugby, Warwickshire, EnglandDied7 October 2001(2001-10-07) (aged 46)Waxahachie, Texas, U.S.Cause of deathBallistic traumaResting placeOak Grove Memorial Gardens (Irving, Texas)Occupation(s)Professional wrestler, promoter, trainer, judokaSpouses Toni Adams (m. 1984;...



