Church of God (Cleveland, Tennessee)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
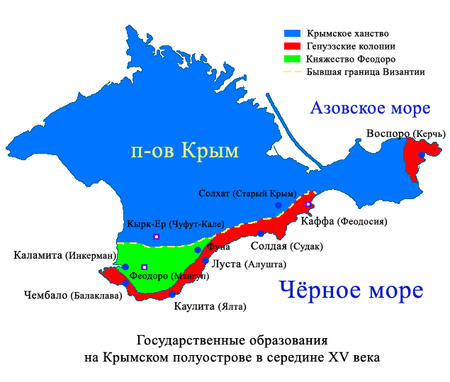
Талассокра́тия (от др.-греч. θάλασσα «море» + κράτος «власть») — подтип государства (античного, средневекового или современного), вся экономическая, политическая и культурная жизнь которого, вследствие недостатка земельных ресурсов или особого географического положени�...

ATEEZ에이티즈Informasi latar belakangAsalKorea SelatanGenreK-popTahun aktif2018–sekarangLabel KQ Entertainment RCA Records[1] Legacy Nippon Columbia[2] Situs web ateez.kqent.com ateez-official.jp Anggota Park Seonghwa Kim Hongjoong Jeong Yunho Kang Yeosang Choi San Song Mingi Jung Wooyoung Choi Jongho ATEEZ (PR: eɪ-tiˈz) (Hangul: 에이티즈 RR: eitijeu), adalah sebuah grup vokal laki-laki 8 anggota asal Korea Selatan yang berada di bawah naungan KQ Entertainment. Gru...

У Вікіпедії є статті про інші населені пункти з такою назвою: Устя. село Устя Герб Устя Пам'ятник на честь Богородиці Країна Україна Область Тернопільська область Район Чортківський район Громада Мельнице-Подільська селищна громада Основні дані Населення 1 099 Територі

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (سبتمبر 2023) الاستعلاء الهاشمي هو أيديولوجية عنصرية في العالم الإسلامي، تقوم على الافتراض الديني بأن عائلة النبي محمد وأحفادهم متفوقون بشكل أساسي على غيرهم من المسلمي�...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’Ukraine. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Descente Saint-André Le musée Ivan Kavaléridzé sur la descente Saint-André. Situation Coordonnées 50° 27′ 35″ nord, 30° 30′ 55″ est Pays Ukraine Ville KKiev Histoire Protection Registre national des monuments d'Ukraine[1],[2] Géolocalisation sur la carte : Kiev m...

بنية التربة (بالإنجليزية: Soil structure) مفهوم يدل على طريقة بناء حبيبات التربة وبقية العناصر المكونة لها (مادة عضوية، ماء، هواء).[1][2][3] هذا المفهوم مكمل لمفهوم قوام التربة. يمكن التمييز بين ثلاثة بنى مختلفة للتربة: بنية متماسكة: وتتميز بوجود طين يجمع بين عناصر الترب...

ガリレオシリーズ > ガリレオ (テレビドラマ) ガリレオ 湯川学の研究室の再現セット(FCGビル内)ジャンル テレビドラマ、ミステリー原作 東野圭吾『ガリレオシリーズ』(文藝春秋)第1シーズン 『探偵ガリレオ』『予知夢』ガリレオΦ『ガリレオの苦悩』第2シーズン 『ガリレオの苦悩』『聖女の救済』『虚像の道化師 ガリレオ7』『禁断の魔術 ガリレオ8』脚本 ...

Pasukan Operasi Khusus Tentara Pembebasan Rakyat中国人民解放军特种部队Zhōngguó Rénmín Jiěfàngjūn TèzhǒngbùduìTambalan Pasukan Operasi Khusus Tentara Pembebasan RakyatAktif1988–sekarangNegara TiongkokAliansi Partai Komunis TiongkokCabangAngkatan DaratAngkatan LautAngkatan UdaraAngkatan RoketTipe unitPasukan khususHimne特种部队之歌(Lagu Pasukan Khusus)PertempuranTindakan anti-perompakan di SomaliaPasukan Operasi Khusus Tentara Pembebasan Rakyat (Hanzi sederhan...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Dancing with the Stars American season 15 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Season of television series Dancing with the Stars: All-StarsSeason 15Promotional poster, featuring All...

Politeknik STIA LAN MakassarNama sebelumnyaSekolah Tinggi llmu Administrasi LANJenisPoliteknik, Perguruan tinggi kedinasanLembaga indukLembaga Administrasi NegaraDirekturDr. Sulaeman Fattah, M.SiAlamatJalan Andi Pangerang Pettarani No. 61, MakassarSitus webhttps://poltek.stialanmakassar.ac.id/ Politeknik STIA LAN Makassar atau dulunya disebut Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Administrasi LAN adalah perguruan tinggi yang dikelola oleh Lembaga Administrasi Negara (LAN) dan terletak di Makassar, Sulawesi Sel...

مديرية وشحة - مديرية - تقسيم إداري البلد اليمن[1] العاصمة وشحة [لغات أخرى][2] المحافظة محافظة حجة إحداثيات 16°15′00″N 43°20′00″E / 16.25°N 43.3333°E / 16.25; 43.3333 [3] السكان التعداد السكاني 2004 السكان 62٬617 • الذكور 33٬113 • الإناث 29٬...

Group of dialects of Bulgarian This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Rup dialects – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (Decemb...

Estonian singer Maarja Nuut at the Great Escape Festival in Brighton area in 2022 Maarja Nuut at the Viljandi Folk Music Festival (2016) Maarja Nuut (born 1986) is an Estonian singer and violinist. After first studying classical music, she turned to folk, adopting the village style of traditional Estonian songs. She debuted as a solo artist in 2013, winning the Artists Prize at the Tallinn Music Week. In 2016, she began to collaborate with Hendrik Kaljujärv (aka Ruum), who creates his own ab...

17th-century French painter Charles Alphonse du Fresnoy, Allegory of Painting, Musée des Beaux-Arts, Dijon, 1650 Charles Alphonse du Fresnoy (1611 – 16 January 1668), French painter and writer on his art. Du Fresnoy was born in Paris, son of an apothecary. He was destined for the medical profession, and well educated in Latin and Greek; but, having a natural propensity for the fine arts, he would not apply to his intended vocation, and was allowed to learn the rudiments of design under Per...

Yutuk batok Yutuk batok (Hippa adactyla)dari pantai Citepus, Palabuhanratu, Sukabumi Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Arthropoda Subfilum: Crustacea Kelas: Malacostraca Ordo: Decapoda Infraordo: Anomura Superfamili: Hippoidea Famili: Hippidae Genus: Hippa Spesies: H. adactyla Nama binomial Hippa adactylaFabricius, 1787[1] Sinonim Remipes testudinarius Latreille, 1806[2] Remipes denticulatifrons White, 1847 Yutuk batok (Hippa adactyla Fabricius) adalah sejenis ...

Maison Marcel DepelsenaireLa façade principale vers le boulevard AudentPrésentationArchitecte Marcel DepelsenaireConstruction 1923Commanditaire Marcel DepelsenaireLocalisationPays BelgiqueRégion Région wallonneProvince Province de HainautCommune CharleroiAdresse boulevard Audent, 406000 CharleroiCoordonnées 50° 24′ 33″ N, 4° 26′ 47″ Emodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata La maison personnelle de l'architecte Marcel Depel...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Stabat Mater (homonymie). Page titre de la partition du Stabat Mater. Souvenir de l'interprétation du 12 septembre 1884 à Worcester, avec les signatures d'Antonín Dvořák et des membres de l'orchestre Le Stabat Mater (opus 58, B.71) est une œuvre pour soli, chœur et orchestre du compositeur tchèque Antonín Dvořák. Genèse Alors qu'il est encore peu connu en dehors de son pays d'origine, le Stabat Mater va contribuer à faire connaître l'auteur sur ...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Action of 17 July 1628 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2018) Action of 17 July 1628Part of Anglo-French War (1627–1629)Date17 July 1628LocationSt. Lawrence River, near present-day Rimouski, QuebecResult English victoryBellige...

Museum in Sabah, Malaysia Agnes Keith HouseRumah Agnes KeithFormer nameNewlandsEstablished26 April 2004 (2004-04-26)LocationSandakan, SabahCoordinates5°50′33.77″N 118°06′58.82″E / 5.8427139°N 118.1163389°E / 5.8427139; 118.1163389TypeHistoric houseOwnerSabah Museum Agnes Keith House (formerly known as the Newlands) (Malay: Rumah Agnes Keith) is a historic house museum in Sandakan, Sabah, Malaysia. The museum is named after Agnes Newton Keith,...

This article is about the municipality in West Bengal, India. For other uses, see Bardhaman (disambiguation). City in West Bengal, IndiaBardhaman BurdwanCityBurdwan City at nightNickname: Royal Heritage City of West BengalBardhamanShow map of West BengalBardhamanShow map of IndiaBardhamanShow map of AsiaCoordinates: 23°14′N 87°52′E / 23.233°N 87.867°E / 23.233; 87.867Country IndiaState West BengalDistrictPurba BardhamanGovernment • TypeMun...


