Politics of the Republic of Artsakh, a largely unrecognised state in the south Caucasus
This article is about recent and past political developments in Artsakh. For the Artsakh government, see
Government of Artsakh.
Politics of Artsakh took place within the constraints of a written constitution, approved by a popular vote, that recognises three branches of government: executive, legislative and judicial. The executive branch of government was exercised within a framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Artsakh was both the head of state and the head of government. The legislative branch of government was composed of both the Government and the National Assembly. Elections to the National Assembly were on the basis of a multi-party system. As of 2009, the American-based non-governmental organisation, Freedom House, ranks Artsakh above both Armenia and Azerbaijan in terms of political and civil rights.[1][2][3] The republic was de facto independent and de jure a part of Azerbaijan. None of the elections in Artsakh were recognised by international bodies such as the OSCE Minsk Group, the European Union or the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. Both Azerbaijan and Turkey had condemned the elections and called them a source of increased tensions.[4][5][6]
Following the Azerbaijani offensive on 19 September 2023, Artsakh agreed to dissolve itself by 1 January 2024,[7] however instead of dissolving, they established a government-in-exile in Yerevan, Armenia.[8] The Prime Minister of Armenia, Nikol Pashinyan, has since severely opposed the government-in-exile's existence in Armenia.[9][10]
Executive branch
 Arayik Harutyunyan
Arayik Harutyunyan
4th President of the Republic
The President was directly elected for a five-year term, by popular vote.
Current government
 Grigori Martirosyan
Grigori Martirosyan
State Minister of the Republic
Legislative branch
 Artsakh Presidential Palace
Artsakh Presidential Palace
 Ashot Ghulian
Ashot Ghulian
Speaker of the National Assembly
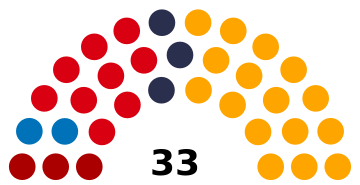
The National Assembly (Azgayin Zhoghov) had 33 members who were elected for a five-year term by Party-list proportional representation. Artsakh had a multi-party system, with numerous political parties in which no one party often had a chance of gaining power alone, and parties had to work with each other to form coalition governments.
Judicial branch
Narine Narimanyan was the last Head of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Artsakh.
Latest elections
Presidential election
| Candidate | Party | First round | Second round |
|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % |
|---|
| Arayik Harutyunyan | Free Motherland - UCA Alliance | 36,076 | 49.17 | 39,860 | 88.01 |
| Masis Mayilyan | Independent | 19,360 | 26.39 | 5,428 | 11.99 |
| Vitaly Balasanyan | Justice | 10,855 | 14.79 | |
| David Ishkhanyan | Armenian Revolutionary Federation | 1,873 | 2.55 | |
| Ashot Ghulian | Democratic Party of Artsakh | 1,683 | 2.29 | |
| Hayk Khanumyan | National Revival | 962 | 1.31 | |
| Vahan Badasyan | United Armenia Party | 743 | 1.01 | |
| David Babayan | Artsakh Conservative Party | 587 | 0.80 | |
| Ruslan Israelyan | Generation of Independence Party | 371 | 0.51 | |
| Christine Balayan | Independent | 202 | 0.28 | |
| Ashot Dadayan | Independent | 198 | 0.27 | |
| Bella Lalayan | Independent | 162 | 0.22 | |
| Sergey Amiryan | Independent | 160 | 0.22 | |
| Melsik Poghosyan | Independent | 141 | 0.19 | |
| Total | 73,373 | 100.00 | 45,288 | 100.00 |
|
| Valid votes | 73,373 | 96.55 | 45,288 | 96.02 |
|---|
| Invalid/blank votes | 2,622 | 3.45 | 1,876 | 3.98 |
|---|
| Total votes | 75,995 | 100.00 | 47,164 | 100.00 |
|---|
| Registered voters/turnout | 104,866 | 72.47 | 104,777 | 45.01 |
|---|
| Source: CEC, CEC |
Parliamentary election
 Logo of the
Logo of the
Free Motherland party
 |
|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– |
|---|
| Free Motherland - UCA Alliance | 30,015 | 40.80 | 16 | +1 |
| United Motherland | 17,683 | 24.04 | 9 | New |
| Justice | 5,867 | 7.98 | 3 | New |
| Armenian Revolutionary Federation | 4,758 | 6.47 | 3 | –4 |
| Democratic Party of Artsakh | 4,314 | 5.86 | 2 | –4 |
| New Artsakh Alliance | 3,385 | 4.60 | 0 | New |
| National Revival | 2,175 | 2.96 | 0 | 0 |
| Artsakh Conservative Party | 2,156 | 2.93 | 0 | New |
| Artsakh Revolutionary Party | 1,325 | 1.80 | 0 | New |
| United Armenia Party | 930 | 1.26 | 0 | New |
| Generation of Independence Party | 551 | 0.75 | 0 | New |
| Communist Party of Artsakh | 402 | 0.55 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 73,561 | 100.00 | 33 | 0 |
|
| Valid votes | 73,561 | 96.82 | |
|---|
| Invalid/blank votes | 2,419 | 3.18 | |
|---|
| Total votes | 75,980 | 100.00 | |
|---|
| Registered voters/turnout | 104,866 | 72.45 | |
|---|
| Source: CEC, Armenanews |
Political parties
Below is a list of former political parties in Artsakh. The region had a multi-party system with numerous political parties, in which no one party often has a chance of gaining power alone, and parties must work with each other to form coalition governments. The following parties won seats in the National Assembly following the 31 March 2020 Artsakhian general election (total 33 seats):
The extra-parliamentary political parties which had no seats in the National Assembly, are listed below:
See also
References
- ^ freedomhouse.org: Map of Freedom in the World, Freedom House, 2009
- ^ freedomhouse.org: Map of Freedom in the World, Freedom House, 2009
- ^ freedomhouse.org: Map of Freedom in the World, Freedom House, 2009
- ^ "EU does not recognize 'elections' in Nagorno Karabakh". News.Az. 1 May 2015. Retrieved 7 June 2016.
- ^ Mustafa Pazarlı. "US will not recognize Nagorno-Karabakh's elections". Videonews.us. Retrieved 7 June 2016.
- ^ Mushvig Mehdiyev. "OIC condemns "elections" in Nagorno-Karabakh as illegal". AzerNews.az. Retrieved 7 June 2016.
- ^ "Nagorno-Karabakh Republic will cease to exist from Jan 1 2024 - Nagorno-Karabakh authorities". Reuters. 2023-09-28. Archived from the original on 2023-09-28. Retrieved 2023-09-28.
- ^ "Nagorno-Karabakh dissolution not valid, says Armenian separatist leader". France 24. 2023-12-22. Retrieved 2024-10-10.
- ^ "Pashinian Slams, Warns Karabakh Leaders". Radio Free Europe. Archived from the original on July 21, 2024. Retrieved July 21, 2024.
- ^ "Pashinyan Attacks Artsakh Government in Exile". Oragark. Archived from the original on July 21, 2024. Retrieved July 21, 2024.
External links
|
|---|
| Sovereign states | |
|---|
States with limited
recognition | |
|---|
Dependencies and
other entities | |
|---|
| Other entities | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Sovereign states | |
|---|
States with limited
recognition | |
|---|
Dependencies and
other entities | |
|---|
| Other entities | |
|---|