Robert Hanbury Brown
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Содержание 1 Административно-территориальное устройство 2 Муниципальное устройство 2.1 Городские округа и муниципальные районы 2.2 Городские и сельские поселения 2.2.1 Ижемский муниципальный район 2.2.2 Княжпогостский муниципальный район 2.2.3 Койгородский муниципальный райо...
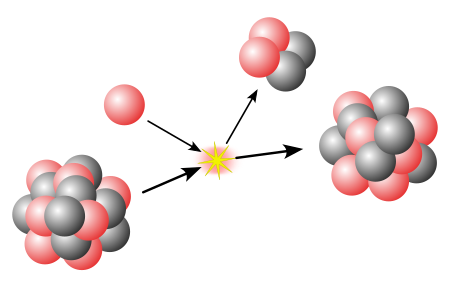
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Mirror nuclei – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Nuclear physics Nucleus Nucleons p n Nuclear matter Nuclear force Nuclear structure Nuclear reaction Models of the nucleus Liquid dr...
هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أغسطس 2012) الأصغران اسم عربي يُقصد به القلب واللسان. يقول المثل العرب...

Juan de Cervantes Información personalNacimiento 24 de junio de 1553jul. México Fallecimiento 13 de septiembre de 1614jul. (61 años)Antequera (España) Religión Iglesia católica Información profesionalOcupación Sacerdote católico y obispo católico (desde 1609) Cargos ocupados Obispo de Antequera (desde 1608) [editar datos en Wikidata] Juan de Cervantes (México, 24 de junio de 1563-Oaxaca, Oaxaca, 13 de septiembre de 1614), fue un criollo mexicano doctorado en sag...

Coto C.I.C.S.A Hipermercado Coto, sucursal Munro, provincia de Buenos AiresTipo Centro Integral de Comercialización Sociedad Anónima (C.I.C.S.A)Campo supermercadoIndustria Supermercadismo - RetailFundación 10 de septiembre de 1970 (53 años)Fundador Alfredo CotoSede central Paysandú 1842, Buenos Aires, ArgentinaMarcas Coto y Ciudad del Lago (comestibles) y TOP (aparatos eléctricos)Productos mini, súper e hipermercadosIngresos USD 2300 millones[cita requerida]Propietario Alfred...

Australian opinion polling brand This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Newspoll – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) NewspollHeadquartersAustraliaServicesresearchWebsitewww.theaustralian.com.au/nation/newspoll Newspoll is an...

Republik GabonRépublique gabonaise (Prancis) Bendera Lambang Semboyan: Union, Travail, Justice (Prancis: Persatuan, Pekerja, Keadilan)Lagu kebangsaan: La ConcordeTampilkan globeTampilkan peta AfrikaIbu kota(dan kota terbesar)Libreville0°23′N 9°27′E / 0.383°N 9.450°E / 0.383; 9.450Bahasa resmiPrancisBahasa vernakular Daftar Teke Fang Punu Nzebi Agama (2012)[1]82.0% Kekristenan—42.3% Katolik Roma—27.4% Protestan—12.3% Kekristenan lainnya9...

فونديه علم شعار الاسم الرسمي (بالفرنسية: Vendée) الإحداثيات 46°40′14″N 1°25′36″W / 46.670556°N 1.426667°W / 46.670556; -1.426667 [1] تاريخ التأسيس 4 مارس 1790 تقسيم إداري البلد فرنسا[2][3] التقسيم الأعلى بايي دو لا لوار العاصمة لاروش سور يون خص

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أكتوبر 2019) أ. تشارلز مولر معلومات شخصية الميلاد سنة 1953 (العمر 69–70 سنة) لونغ آيلند مواطنة الولايات المتحدة الحياة العملية شهادة جامعية دكتوراه المهنة لغو

Community college in Tennessee This article is about the college in Jackson, Tennessee. For the college in Jackson, Michigan, see Jackson College. For the college in Jackson, Mississippi, see Jackson State College. For other uses, see Jackson College (disambiguation). Jackson State Community CollegeTypePublic community collegeEstablished1967; 56 years ago (1967)Parent institutionTennessee Board of RegentsPresidentCarol A. RothsteinLocationJackson, Tennessee, U.S.35°38′42�...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Tujuh tradisi teori komunikasi merupakan gambaran teoretis mengenai tradisi komunikasi yang didasari oleh kehidupan yang nyata. Tujuh tradisi teori komunikasi ditemukan oleh Robert Craig. Craig menyatakan bahwa komunikasi merupakan bentuk pengalaman, ...

アングロ・アメリカンAnglo American plc 種類 株式会社(公開会社)市場情報 LSE: AALJSE: AGLFTSE 100 Component略称 AAC本社所在地 イギリスロンドン設立 1917年(ヨハネスブルグ)Anglo American Corporationとして1999年(ロンドン)Anglo American plcとして業種 金属と鉱業代表者 ジョン・パーカー(会長)マーク・キューティファニ(CEO)売上高 262億43000万ドル(2017年)営業利益 52億42000�...

Кіндрат Гаврилович Клименко Народження 25 жовтня 1913(1913-10-25)Шура-Копіївська (зараз Вінницька область)Смерть 10 березня 1945(1945-03-10) (31 рік)НімеччинаПоховання Західнопоморське воєводствоКраїна СРСРПриналежність Радянська арміяРід військ кавалеріяРоки служби 1934–1945...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع مروي (توضيح). مروي (مدينة تاريخية) موقع اليونيسكو للتراث العالمي الدولة السودان النوع ثقافي المعايير ii, iii, vi, v رقم التعريف 1336 المنطقة مواقع التراث العالمي ** الإحداثيات 16°56′07″N 33°45′03″E / 16.935138888889°N 33.75075°E / 16.935138888889; 33.75075 تاريخ الاعت...

1971 film Le ChatFilm posterDirected byPierre Granier-DeferreWritten byPierre Granier-DeferrePascal JardinGeorges SimenonProduced byRaymond DanonMaurice JacquinStarringJean GabinSimone SignoretAnnie CordyCinematographyWalter WottitzEdited byNino BaragliMusic byPhilippe SardeRelease date 24 April 1971 (1971-04-24) Running time86 minutesCountriesFranceItalyLanguageFrenchBudget$6.2 million[1] Le Chat ([lə ʃa], The Cat) is a 1971 French-language drama film directe...

This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Malta at the European Games – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Sporting event delegationMalta at theEuropean GamesIOC codeMLTNOCMalta Olympic CommitteeWebsitenocmalta.org (in English)Medals Gold 0 Silver 0 Bronze 0 Total 0 ...

Christian Orthodox Church in Moldova, under the Moscow Patriarchate This article is about one of the Orthodox churches in Moldova. For other uses, see Moldovan Orthodox Church (disambiguation). Metropolis of Chișinău and All Moldova19th century Nativity Cathedral in Chișinău.LocationTerritory MoldovaHeadquartersChișinău, MoldovaStatisticsPopulation- Total1,286 communitiesInformationDenominationEastern OrthodoxSui iuris churchMoscow Patriarchate(Autonomous Metropolis)Establishe...

2006 American filmInfamousTheatrical release posterDirected byDouglas McGrathScreenplay byDouglas McGrathBased onTruman Capote: In Which Various Friends, Enemies, Acquaintances and Detractors Recall His Turbulent Career by George PlimptonProduced byChristine VachonJocelyn HayesStarring Toby Jones Sandra Bullock Daniel Craig Peter Bogdanovich Jeff Daniels Hope Davis Gwyneth Paltrow Isabella Rossellini Juliet Stevenson Sigourney Weaver Lee Pace CinematographyBruno DelbonnelEdited byCamilla Toni...

Serbian video game developer This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) A major contributor to this article appears to have a close connection with its subject. It may require cleanup to comply with Wikipedia's content policies, particularly neutral point of view. Please discuss further on the talk page. (December 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) This articl...

Examination of the heart's electrical activity ECG and EKG redirect here. For other uses, see ECG (disambiguation) and EKG (disambiguation). Not to be confused with other types of electrography or with echocardiography. ElectrocardiographyECG of a heart in normal sinus rhythmICD-10-PCSR94.31ICD-9-CM89.52MeSHD004562MedlinePlus003868[edit on Wikidata] Use of real time monitoring of the heart in an intensive care unit in a German hospital (2015), the monitoring screen above the patient displ...