Battle of Peregonovka
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Mercury(II) thiocyanate Names Other names Mercuric thiocyanateMercuric sulfocyanate Identifiers CAS Number 592-85-8 Y 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ECHA InfoCard 100.008.886 EC Number 209-773-0 PubChem CID 11615 UNII 3JNH1DM7IF Y CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID7060469 InChI InChI=1S/2CHNS.Hg/c2*2-1-3;/h2*3H;/q;;+2/p-2Key: GBZANUMDJPCQHY-UHFFFAOYSA-L SMILES C(#N)[S-].C(#N)[S-].[Hg+2] Properties Chemical formula Hg(SCN)2 Molar mass 316.755 g/mol Appearance ...

English soldier and diplomat Sir John St JohntArms of John St John: Argent, on a chief gules two mullets orBorn1230sDied6 September 1302Lochmaben, Dumfriesshire, ScotlandBuriedOld Basing, Hampshire, EnglandSpouse(s)Alice FitzPiersIssueJohn St John, 1st Baron St JohnEdward St JohnAgnes St JohnFatherRobert St JohnMotherAgnes Cantilupe Sir John St John (died 1302), of Basing in Hampshire, was an English landowner, soldier, administrator and diplomat who was a close confidant of King Edward I, se...

صورة توضح بناء المجتمعات بناء المجتمعات (بالإنجليزية: community building) هو ذلك المجال الذي يضم مجموعة من الممارسات الموجّهة نحو خلق وتعزيز الحس الجماعي بين الأفراد في مناطق معينة (مثل الأحياء ومناطق الجوار) أو ضمن المجموعات ذات الاهتمامات المشتركة. وهذا المصطلح «بناء الجماعة» �...

Triatletas nadando en aguas abiertas. La natación en aguas abiertas es una disciplina de natación que consiste en nadar en lugares abiertos como el mar, lagos o ríos. El comienzo de la era moderna de la natación en aguas abiertas se considera el 3 de mayo de 1810, cuando Lord Byron nadó varios kilómetros para cruzar el estrecho de los Dardanelos desde Europa hasta Asia. En la primera edición de los Juegos Olímpicos las competiciones de natación se realizaron en la bahía de Zea. En e...

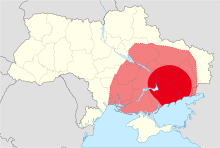
Ця стаття має кілька недоліків. Будь ласка, допоможіть удосконалити її або обговоріть ці проблеми на сторінці обговорення. Ця стаття недостатньо ілюстрована. Ви можете допомогти проєкту, додавши зображення до цієї статті. (січень 2020) Пам'ятник воїнам-інтернаціоналіст

Untuk jenis sayur, lihat Bawang putih. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Bawang Merah Bawang Putih (disambiguasi). Bawang PutihSutradara F. Sutrisno Produser Bucuk Suharto Ditulis oleh Titiek Puspa PemeranTanty JosephaTitiek PuspaIta SitompulBroery PesolimaKris BiantoroSaid EffendyNanien Sudiar Dewi Yull Elly KasimWirdaningsihIskakBudiman (artis)Penata musikMus MualimSinematograferFES TariganTanggal rilis1974Durasi101 menitNegara IndonesiaBahasa Indonesia Bawang Putih adalah film drama musikal...

موتي (بالهولندية: Timo Romme) معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة (بالهولندية: Timotheus Romme) الميلاد 23 مارس 1987 (36 سنة) أمستردام مواطنة مملكة هولندا الحياة الفنية النوع إلكتروهاوس شركة الإنتاج سبينن ريكوردز المهنة منتج أسطوانات، وملحن، ودي جيه، وموسيقي تسجيل

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Wellesley, Massachusetts – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Town in Massachusetts, United StatesWellesley, MassachusettsTownWellesley Town Hall SealLocation of Wellesley in Norfolk ...

Building in New York City Not to be confused with the South Yuba Canal Office, formerly called the Potter Building. Potter BuildingSeen from across Park Row (2012)General informationLocationFinancial District, Manhattan, New YorkAddress35–38 Park Row or 145 Nassau Street, New York, NY 10038Coordinates40°42′42″N 74°00′24″W / 40.71167°N 74.00667°W / 40.71167; -74.00667Construction started1883Completed1886Technical detailsFloor count11Design and construction...

Site of Special Scientific Interest in Gloucestershire For other uses, see Hobbs Quarry. Hobbs Quarry, LonghopeSite of Special Scientific InterestWood anemones (Anemone nemorosa) in a Forest of Dean woodLocation within GloucestershireLocationGloucestershireGrid referenceSO695195Coordinates51°52′25″N 2°26′37″W / 51.873683°N 2.443701°W / 51.873683; -2.443701InterestBiological/GeologicalArea1 hectareNotification1966Natural England website Hobbs Quarry, Longhop...

1st Miss Grand Angola competition, beauty pageant edition Miss Grand Angola 2023Eugénia das Neves, the winner of the contestDateSeptember 2, 2023PresentersBráulio AndersonWhitney ShikongoEntertainmentBassHeróide Dos PrazeresVenueEpic Sana Hotel, LuandaBroadcasterYouTubeEntrants10Placements7WinnerEugénia das Neves(Luanda)2024 → External videos Miss Grand Angola 2023 Grand final competition, on September 2, 2023, Youtube Video Miss Grand Angola 2023 was the inaugural edition of t...

Panerusan KulonDesaNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TengahKabupatenBanjarnegaraKecamatanSusukanKode pos53475Kode Kemendagri33.04.01.2006 Jumlah penduduk-Kepadatan- IPM/HDI: 0,742 ( Tinggi) Panerusan Kulon adalah desa di kecamatan Susukan, Banjarnegara, Jawa Tengah, Indonesia. Pranala luar (Indonesia) Keputusan Menteri Dalam Negeri Nomor 050-145 Tahun 2022 tentang Pemberian dan Pemutakhiran Kode, Data Wilayah Administrasi Pemerintahan, dan Pulau tahun 2021 (Indonesia) Peraturan Menteri Dalam ...

Ця стаття потребує істотної переробки. Можливо, її необхідно доповнити, переписати або вікіфікувати. Пояснення причин та обговорення — на сторінці Вікіпедія: Статті, що необхідно поліпшити. Тому, хто додав шаблон: зважте на те, щоб повідомити основних авторів статті п�...

Fundamental rights belonging to all humans For other uses, see Human rights (disambiguation). Magna Carta or Great Charter was one of the world's first documents containing commitments by a sovereign to his people to respect certain legal rights. Rights Theoretical distinctions Claim rights and liberty rights Individual and group rights Natural rights and legal rights Negative and positive rights Human rights Civil and political Economic, social and cultural Three generations Rights by benefi...

1957 film A Matter of DignityDVD coverDirected byMichael CacoyannisWritten byMichael CacoyannisStarringEllie LambetiCinematographyWalter LassallyEdited byGiorgos TsaoulisRelease date 1958 (1958) Running time112 minutesCountryGreeceLanguageGreek A Matter of Dignity (Greek: Το τελευταίο ψέμα, translit. To teleftaio psema) is a 1958 Greek drama film directed by Michael Cacoyannis. It was entered into the 1958 Cannes Film Festival.[1] Plot The Pellas are magnates ...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (يونيو 2020) كأس آسيا للجودو 1984معلومات عامةالرياضة جودو البطولة Asian Judo Championships (en) الفترة 1984 البداية 1 أبريل 1984 النهاية 4 أبريل 1984 البلد اليابان المكان مدينة الكويت تعديل - �...

Racing Club de LensCalcio Les Sang et Or Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Terza divisa Colori sociali Rosso, oro Inno Les CoronsPierre Bachelet Dati societari Città Lens Nazione Francia Confederazione UEFA Federazione FFF Campionato Ligue 1 Fondazione 1905 Proprietario Sarl Solférino Presidente Joseph Oughourlian Allenatore Franck Haise Stadio Stade Bollaert-Delelis(38.223 posti) Sito web www.rclens.fr Palmarès Titoli di Francia 1 Trofei nazionali 1 Coppe di Lega fran...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (مارس 2021) ريهام الهور معلومات شخصية الميلاد 8 مارس 1977 (46 سنة)[1] القنيطرة مواطنة المغرب الحياة العملية المدرسة الأم جامعة ابن طفيل المهنة كاريكاتيرية، &#...

Див. також: Список призерів чемпіонатів України з легкої атлетики в приміщенні (жінки) Цей список включає призерів чемпіонатів України з легкої атлетики в приміщенні в чоловічих дисциплінах за всі роки їх проведення. Зміст 1 Чинна програма 1.1 60 метрів 1.2 200 метрів 1.3 400 метр�...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento edizioni di competizioni calcistiche non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Allsvenskan 2004 Competizione Allsvenskan Sport Calcio Edizione 80ª Organizzatore SvFF Date dal 3 aprile 2004al 30 ottobre 2004 Luogo Svezia Partecipanti 14 Formula Giron...